Kollmorgen UDFBs
A KollmorgenUDFB![]() "User Defined Function Block"
UDFB can be used as a sub-function block in another program of the application. It is described using FBD, LD, ST or IL language. Input / output parameters of a UDFB (as well as private variables) are declared in the variable editor as local variables of the UDFB is a pre-defined function block created by Kollmorgen to simplify certain tasks or demonstrate a particular function. A Kollmorgen UDFB
"User Defined Function Block"
UDFB can be used as a sub-function block in another program of the application. It is described using FBD, LD, ST or IL language. Input / output parameters of a UDFB (as well as private variables) are declared in the variable editor as local variables of the UDFB is a pre-defined function block created by Kollmorgen to simplify certain tasks or demonstrate a particular function. A Kollmorgen UDFB![]() "User Defined Function Block"
UDFB can be used as a sub-function block in another program of the application. It is described using FBD, LD, ST or IL language. Input / output parameters of a UDFB (as well as private variables) are declared in the variable editor as local variables of the UDFB must be instantiated before it may be used. The code inside a Kollmorgen UDFB can be modified by creating an unlocked copy in the subprogram section in the project tree..
"User Defined Function Block"
UDFB can be used as a sub-function block in another program of the application. It is described using FBD, LD, ST or IL language. Input / output parameters of a UDFB (as well as private variables) are declared in the variable editor as local variables of the UDFB must be instantiated before it may be used. The code inside a Kollmorgen UDFB can be modified by creating an unlocked copy in the subprogram section in the project tree..
| Name | Description |
| FB_AKDFltRpt | Outputs AKD fault information |
| FB_AxisPlsPosModulo | Used for any position of a modulo axis in both directions |
| FB_AxisPlsPosNoModulo | Used for any position of a non-modulo axis in both directions |
| FB_Cylinder | Control a cylinder and the Limit Switches. |
| FB_ElapseTime | Keeps track of the time that a Boolean input variable is on. |
| FB_FirstOrderDigitalFilter | Filter an Analog signal. |
| FB_PWDutyOutput | Converts an input range to a duty cycle percentage |
| FB_S700FltRpt | Outputs S700 |
| FB_ScaleInput | Scale DINT to LREAL |
| FB_ScaleOutput | Scale DINT to LREAL |
| FB_TemperaturePID | Provides PID |
| MCFB_AKDFault | Outputs AKD drive fault Information. |
| MCFB_AKDFaultLookup | String message of the corresponding AKD drive fault number |
| MCFB_GearedWebTension | Facilitates dancer and tension control in an electronic geared master/slave machine design |
| MCFB_Jog | Jog an axis in the selected direction at a defined speed |
| MCFB_StepAbsolute | Performs a static homing function by setting Actual Position to the position of an absolute encoder |
| MCFB_StepAbsSwitch | Performs a homing function by searching for an absolute positioned external physical switch |
| MCFB_StepAbsSwitchFastInput | Performs a homing function by searching for an absolute positioned external physical switch |
| MCFB_StepBlock | Performs homing against a physical object, mechanically blocking the movement |
| MCFB_StepLimitSwitch | Performs a single-axis home to a limit switch |
| MCFB_StepLimitSwitchFastInput | Performs a homing function by searching for an external physical switch |
| MCFB_StepRefPulse | Performs homing by searching for Zero pulse, Marker, or reference pulse in encoder |
| MLFB_HomeFindHomeFastInput | Performs a single-axis home to a limit switch connected to a High Speed Input |
| MLFB_HomeFindHomeFastInputModulo | Performs a single-axis home to a limit switch connected to a High Speed Input |
| MLFB_HomeFindHomeInput | Fast Homing |
| MLFB_HomeFindHomeInputThenZeroAngle | Fast Homing to a home switch + Zero angle |
| MLFB_HomeFindLimitFastInput | Homing to a limit switch |
| MLFB_HomeFindLimitFastInputModulo | Homing to a limit switch: Modulo mode |
| MLFB_HomeFindLimitInput | Homing to a limit switch |
| MLFB_HomeFindLimitInputThenZeroAngle | Homing to a limit switch + Zero angle |
| MLFB_HomeFindZeroAngle | Homing to a zero-angle reference |
| MLFB_HomeMoveUntilPosErrExceeded | Homing until the position error is exceeded |
| MLFB_HomeMoveUntilPosErrExceededThenZeroAngle | Homing until the position error is exceeded + Zero angle |
| MLFB_HomeUsingCurrentPosition | Homing using the current position |
| MLFB_Jog | Jog in a selected direction at a defined speed |
| MLFB_PlsPosFw | Forward position range indicator |
| MLFB_PlsPosFwBw | Forward/Backward position range indicator |
| MLFB_PlsTimeFw | Forward/Backward position/time range indicator |
| PipeNetwork_FFLD | Used to call the PNCode function block in FFLD POUs |
| ProfilesCode_FFLD | Used to call the ProfilesCode function block in FFLD POUs |
Table 7-50: List of System Kollmorgen UDFBs
How to create an instance
- Open your PLC
 "Programmable Logic Controller"
A Programmable Logic Controller, PLC, or Programmable Controller is a digital computer used for automation of industrial processes, such as control of machinery on factory assembly lines.
Used to synchronize the flow of inputs from (physical) sensors and events with the flow of outputs to actuators and events code
"Programmable Logic Controller"
A Programmable Logic Controller, PLC, or Programmable Controller is a digital computer used for automation of industrial processes, such as control of machinery on factory assembly lines.
Used to synchronize the flow of inputs from (physical) sensors and events with the flow of outputs to actuators and events code - Select the UDFB in the Library tree
- Drag-and-drop the UDFB in the PLC editor to create the instance of the UDFB
An instance of the UDFB has now been created in Subprograms.
-
-
You cannot create the instance of the UDFB directly from the dictionary or from the PLC Editor.
Working with Kollmorgen UDFBs
By default all Kollmorgen UDFBs are protected, meaning they may not be modified or renamed. When a Kollmorgen UDFB is dropped into an instance it is not editable. There are two solutions to make it editable:
- Right click on a Kollmorgen UDFB that has been dropped into an instance (in Subprograms) and select Unlock. This creates an unlocked version of the UDFB with the name "U<sequence number><UDFB name>".
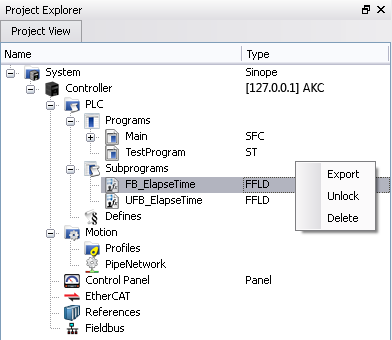
- Instead of dropping a Kollmorgen UDFB into an instance, right click on the UDFB and select Create unlocked copy in Subprograms. This creates an unlocked instance of the UDFB with the name "U<sequence number><Kollmorgen UDFB name>".
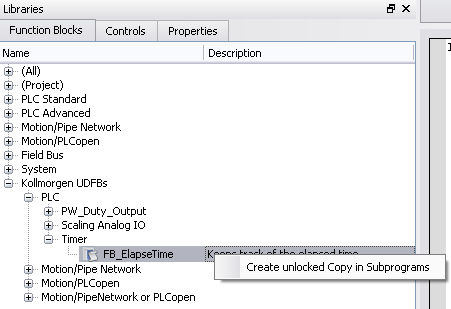
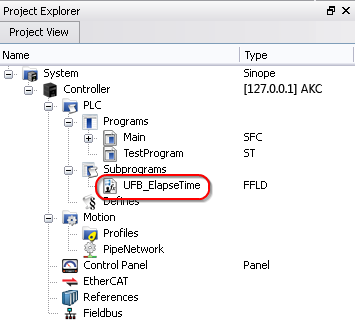
Once a Kollmorgen UDFB has been unlocked it may be renamed and exported by right-clicking on the UDFB. Renamed UDFBs must have unique names. Importing a saved UDFB will increment the UDFB's name.







